
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean, located between Mainland China and Taiwan to the north, the Philippines and Vietnam to the west, and the Malay Peninsula and Singapore to the south. It is bounded by the Chinese provinces of Fujian and Hainan to the east and Guangdong to the north, and the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines to the south. It has an area of about 3,500,000 sq km. The South China Sea is divided into several smaller seas, including the Gulf of Tonkin, the Gulf of Thailand, the Sulu Sea, and the Celebes Sea. The South China Sea is also connected to the East China Sea and the Taiwan Strait by the Luzon Strait. The South China Sea is home to numerous islands, including the Paracel Islands, the Spratly Islands, the Pratas Islands, and the Macclesfield Bank. There are also numerous reefs and shoals, including the Scarborough Shoal, and the Paracel Islands are home to numerous oil and gas fields. The South China Sea is also home to numerous ports, including the Port of Singapore, the Port of Hong Kong, and the Port of Kaohsiung. The South China Sea is also an important military area, with several countries, including China, the United States, and Russia, maintaining significant military presence in the region. The South China Sea is an important area for many industries, including tourism, shipping, and fishing. In recent years, the South China Sea has been the subject of territorial disputes between China and its Southeast Asian neighbors, and tensions between the two sides continue to simmer.

The Caribbean Sea is a large body of water located in the western region of the Atlantic Ocean, bordered by the countries of Mexico and Central America to the west, and the islands of the West Indies to the east. The area of the Caribbean Sea covers an estimated 2,754,000 sq km. This large expanse of water is divided into two sections, the North Atlantic and South Atlantic, each with its own distinct characteristics and ecosystems. The Caribbean Sea is an incredibly diverse environment and contains a variety of habitats. The islands of the West Indies and the continental shelves of Central America and Mexico are home to coral reefs, mangrove swamps, seagrass beds, and oyster beds. These habitats are home to a large variety of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sea turtles, sharks, and many species of fish. The Caribbean Sea is also home to a number of large shipping lanes and is a popular destination for cruise ships. In addition to its natural beauty, the Caribbean Sea is home to numerous cultural sites and archaeological sites, including the legendary underwater city of El Dorado. The Caribbean Sea is connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the Yucatan Channel, which separates the two bodies of water.

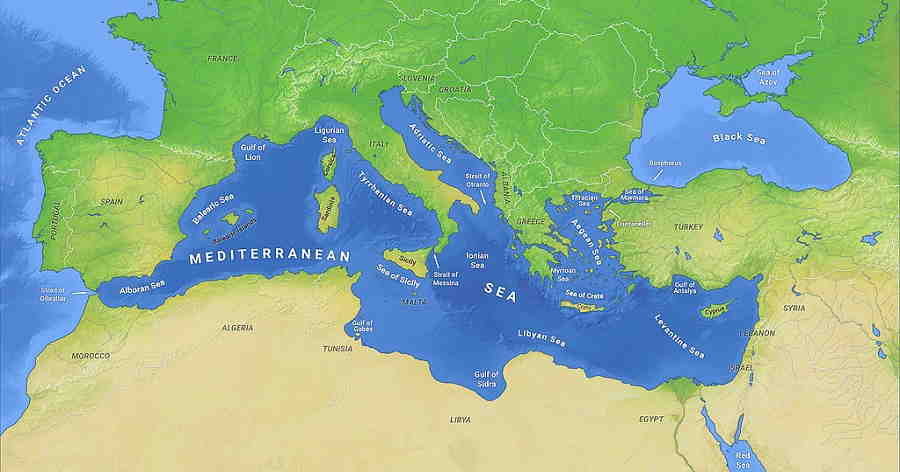
The Mediterranean Sea is a body of water located between Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. It is the world’s largest inland sea, covering an area of approximately 2,500,000 sq km. The Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar and the Sea of Marmara, and to the Red Sea through the Suez Canal. The Mediterranean Sea is divided into two main basins, the western and eastern basins, with the Ionian Sea separating them. The western basin is the larger of the two, covering an area of nearly two million square kilometers. It is bordered by Spain and France to the west, and Italy, Greece, and Turkey to the east. The eastern basin is much smaller, covering an area of about half a million square kilometers and is bordered by Sicily, Tunisia, and Egypt to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the east. The coastline of the Mediterranean Sea is over 15,000 kilometers long and includes numerous islands, including Cyprus, Crete, Corsica, and Malta. The Mediterranean is a major shipping route, connecting Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. It is also a popular tourist destination, with its beaches, resorts, and ancient cities drawing millions of visitors each year.

The Bering Sea is an arm of the Northern Pacific Ocean located between Alaska and Russia. It covers an area of approximately 2,000,000 sq km, making it one of the largest seas in the world. The Bering Sea is bounded by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Sea of Okhotsk to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the south, and the Bering Strait to the west. It is connected to the Arctic Ocean in the north, and is fed by the Alaska Current and the Kamchatka Current. The Bering Sea is home to numerous species of fish, whales, seals, and sea birds. It also supports a variety of subsistence and commercial fisheries, including salmon, pollock, crab, and halibut. Its waters are some of the richest fishing grounds in the world. The Bering Sea is also home to a variety of marine mammals and seabirds, including the endangered Steller's sea cow, the critically endangered spectacled eider, and the threatened spotted seal. The Bering Sea is highly productive, and its nutrient-rich waters are essential to the health of the North Pacific Ocean. The sea is a major source of global carbon dioxide, and its waters are also rich in iron, nitrogen, and other nutrients. The Bering Sea is an important habitat for a wide variety of marine life, and its waters are home to numerous species of fish, whales, seals, and sea birds. The Bering Sea is a dynamic body of water, and its climate is influenced by the surrounding land masses, changing oceanography, and extreme weather events.

The Gulf of Mexico is an oceanic basin located between the United States and Mexico, bordered by the Yucatan Peninsula and the Caribbean Sea. It ihas an area of 1,592,800 sq km. The Gulf of Mexico is home to a diverse range of marine wildlife, including whales, dolphins, manatees, sea turtles, and many species of fish. The Gulf of Mexico is a vital source of food, jobs, and recreation for millions of people around the world. In addition to its abundant marine life, the Gulf of Mexico is home to over 200 species of coral, algae and other marine plants. The Gulf of Mexico is also the major source of oil and natural gas in the United States. Oil and gas reserves in the Gulf of Mexico are estimated to be around 60 billion barrels and over 1 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, respectively.

The Sea of Okhotsk is a body of water located in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It is bordered by the Russian Far East and the Kamchatka Peninsula in the east, the Kuril Islands in the south, and the Sakhalin Island in the north. The Sea of Okhotsk has a total area of about 1,583,000 sq km. The Sea of Okhotsk is one of the most productive fisheries in the world. It is home to a rich biodiversity of marine species, including over 180 species of fish, more than 700 species of invertebrates, and several species of marine mammals. The most important commercial species in the Sea of Okhotsk are pollock, herring, and salmon. The Sea of Okhotsk is also home to a rich variety of seabirds, including black-legged kittiwakes, eared seals, and sea lions. The sea is also home to a variety of whales, including orcas, humpbacks, and gray whales. The Sea of Okhotsk has a wide range of temperatures and is subject to seasonal changes. In the summer months, temperatures reach up to 30°C, while in the winter months, the sea can drop to temperatures as low as -20°C . The Sea of Okhotsk is one of the most important sources of transportation for goods and services in the region.

The East China Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific, located to the east of mainland China and the Korean peninsula. It is bounded to the north by the Korean Peninsula and the Yellow Sea, to the east by the Pacific Ocean, to the south by the South China Sea, and to the west by the Chinese mainland and Taiwan. The East China Sea covers an area of approximately 1,249,000 sq km. The East China Sea begins at the mouth of the Yalu River between China and North Korea, and extends southward to the Japanese Ryukyu Islands, eastward to the Pacific Ocean, and westward to the Taiwan Strait. Its northern border is defined by the Yellow Sea and the Korean Peninsula, while its western border is located along the Chinese mainland and Taiwan. The East China Sea is divided into an inner and an outer sea, with the inner sea located in the north and the outer sea in the south. The main islands of the East China Sea are the Ryukyu Islands of Japan, the Yushan Islands of Taiwan, and the Senkaku Islands of Japan. The East China Sea is one of the most important fishing grounds in the world, and is home to numerous fish species such as tuna, sardines, mackerel, and anchovies.

Hudson Bay is an immense body of water located in the northern part of North America. It lies between the provinces of Quebec and Ontario in Canada, and the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan in the United States. The bay is roughly 1,232,300 sq km in area. The bay is bordered by three distinct landscapes: the Canadian Shield to the north, the Great Lakes to the south, and the Arctic tundra to the east. The bay is fed by thirty-two rivers, of which the largest is the Nipigon River. Hudson Bay is connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Hudson Strait, a narrow channel in the south linking it to the Labrador Sea. The bay is home to a wide variety of wildlife, including polar bears, walruses, seals, whales, and various species of fish. It is also home to over fifty communities of Indigenous peoples, whose traditional way of life has been heavily impacted by the changing climate. The bay is a major shipping lane, connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.

The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean located between the Japanese archipelago and the Asian mainland. It is bordered by the Japanese islands of Hokkaido, Honshu, and Kyushu to the east, the Korean Peninsula to the west, and Russia's Sakhalin Island to the north. The Sea of Japan covers an area of approximately1,007,800 sq km. The Sea of Japan is divided into two distinct basins, the Japan Sea and the East China Sea. The Japan Sea is located in the northern part of the sea, and is bordered by the Russian island of Sakhalin, the Japanese islands of Hokkaido and Honshu, and the Korean Peninsula. The East China Sea is located in the southern part of the sea and is bordered by the Chinese mainland, the Japanese islands of Kyushu and Shikoku, and the Ryukyu Islands. The Sea of Japan is home to a variety of fish species, including the Pacific herring, the walleye pollock, the Japanese anchovy, and the yellowtail.

The Andaman Sea is a marginal sea located in the Indian Ocean, bordered by the Malay Peninsula and Myanmar to the east and north, the Bay of Bengal to the west, and the Nicobar Islands and Andaman Islands to the south. It is located between the Bay of Bengal to the west, the Malay Peninsula to the east, and the Strait of Malacca to the south. The sea has an area of approximately 797,700 sq km. The Andaman Sea is part of the Indian Ocean monsoon system, which brings in heavy rains during the months of October to April. This season is important for the local fishing industry. The northeast monsoon, occurring from December to March, brings in warm and dry air, which is then cooled and humidified by the sea waters. The Andaman Sea is an important fishing ground for both small scale and commercial fishermen, with a variety of fish species such as tuna, sardines, mackerel, scads, groupers, and snappers. The sea also provides a habitat for various species of marine mammals, such as dolphins, whales, and dugongs. The Andaman Sea is also an important shipping route, connecting the east and west coasts of the Indian subcontinent.