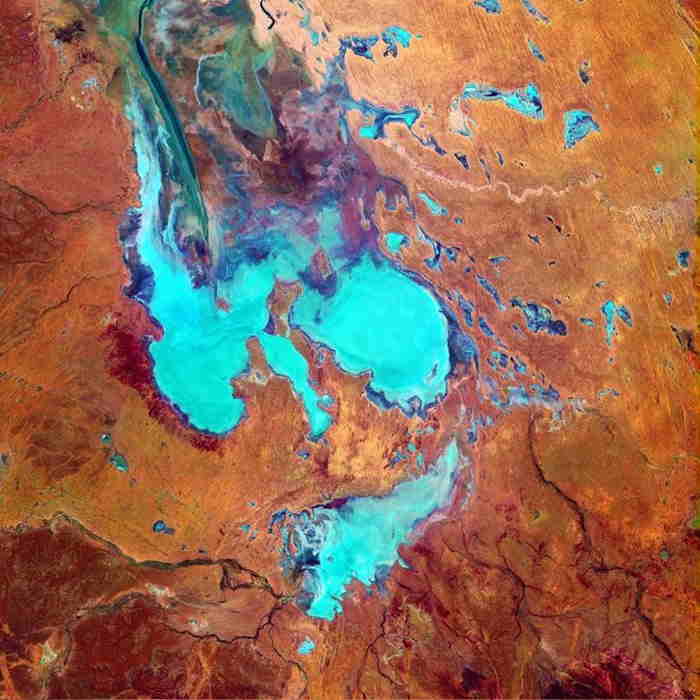

Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre is an immense salt lake located in the heart of the Australian outback. The lake is located in the state of South Australia and is the largest lake in the country, occupying an area of 9,500 square km. It is Australia's lowest point at 15 metres below sea level and is the world's largest salt pan. Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre is an ancient lake, first formed approximately 10,000 years ago. It is fed by the Warburton, Diamantina and Georgina river systems, however the lake is mostly dry due to the low rainfall in the area. When the lake does fill, it is only for a few months at a time, usually following major floods. Despite its vast size, Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre is surprisingly shallow. The lake is covered with salt crust which is up to 10 centimetres thick in some places. Despite its dryness, Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre is a crucial habitat for a number of species. The lake is home to over 70 species of waterbird, including pelicans, swans, ducks and herons.
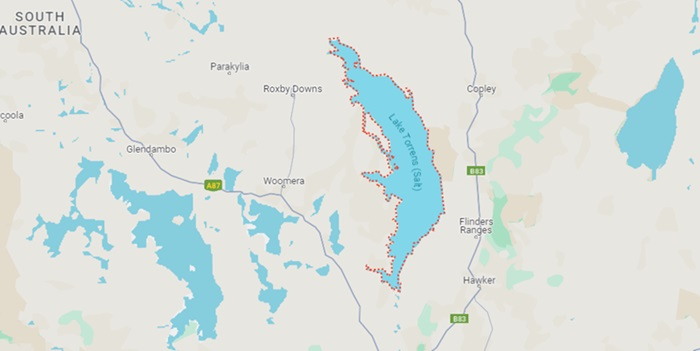
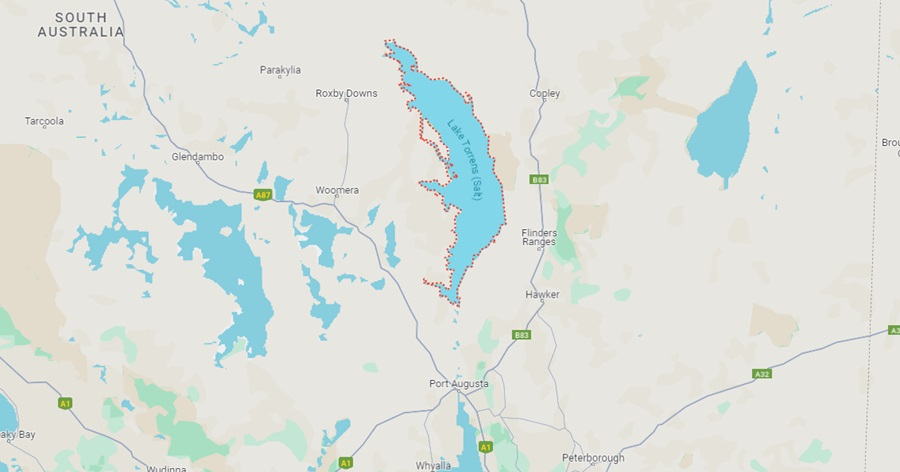
Lake Torrens is a large salt lake located in the northern part of South Australia, near the geographic centre of the continent. It covers an estimated area of about 5745 square km. It is located within the Gawler Ranges National Park and the Lake Torrens Conservation Park. The lake is a shallow and saline endorheic basin. Its maximum depth is about 1 metres. Its shoreline is rocky and its surface is covered with salt crusts. The lake is fed by ephemeral streams, but is not supplied by any major river. It also receives runoff from the surrounding area, which is mostly semi-arid, and evaporates much of the water it receives.
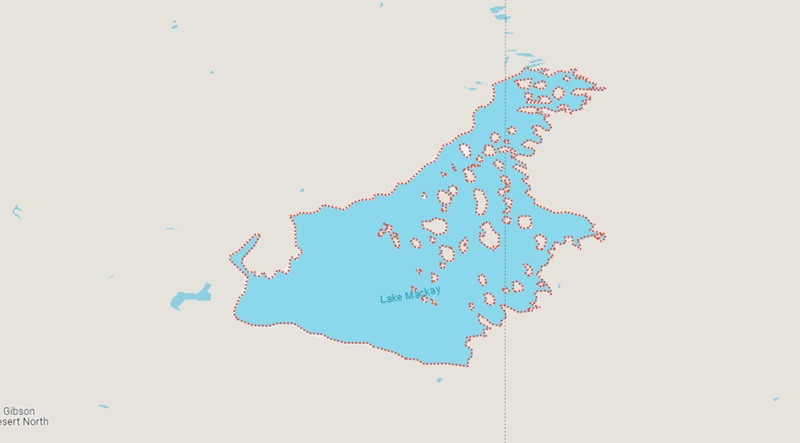
Lake Mackay is an expansive saltwater lake located in the Northern Territory of Australia. The lake spans an area of 3494 square km. It is situated in the Tanami Desert, and is bordered by the Northern Territory, Western Australia and South Australia. The lake is fed by two rivers, the Finke River and the Neales River. These two major water sources feed Lake Mackay’s vast expanse, and the lake is also fed from the smaller tributaries of the larger rivers. The lake is shallow in many areas, with an average depth of only 6 metres. The lake is essentially a large salt pan. The lake is separated into two main sections, the northern section and the southern section. The northern section is the largest of the two, and is home to a variety of fish species, including barramundi, bream and mullet.
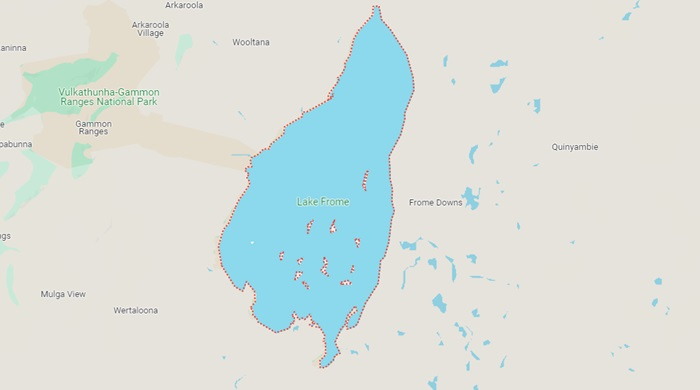
Lake Frome is located in the arid Flinders Ranges of South Australia. It is a large terminal lake, meaning it has no outlet to the ocean, and is fed by a number of seasonal creeks. The lake is located on the Strzelecki Track and is easily accessible from the nearby Wilpena Pound resort. Lake Frome has a surface area of 2596 square km. Its maximum length is about 100 km, and its maximum width is about 40 km. The lake is about 0.5 m deep at its deepest point and is surrounded by grassland, saltbush and low shrubs. The lake is an important habitat for many bird species, particularly wetland birds.
Lake Barlee is a large saline lake located in the Great Sandy Desert region of Western Australia. It is the second largest lake in the region, covering an area of approximately 1980 square km. The lake is a vital part of the ecology of the region, providing a vital habitat for a variety of bird species, as well as other fauna. The lake has an irregular shape, and its surface area varies considerably with the amount of rain that falls in the region. The lake has a maximum length of 80 km and maximum width of 100 km.
Lake Macleod, located in Western Australia, spans approximately 2000 square km. This ephemeral salt lake undergoes significant fluctuations in size, with its surface area varying based on seasonal and climatic conditions. The lake is part of the larger Lake Macleod system, and its expansive salt flats contribute to the unique landscape of the region. The fluctuating water levels and vast salt pans make Lake Macleod a dynamic and visually striking feature in the Australian outback. The lake has an average depth of 1.5 m and a maximum depth of 2.1 m.
Lake Amadeus is a large salt lake located in the Northern Territory of Australia. It icovers an area of approximately 1032 square km and is located approximately 500 kilometers south of Darwin. The lake was formed as a result of seasonal flooding of the Finke River, and is made up of a range of salt pans, sand dunes, and claypans that have been left behind as the lake dried up. The lake is a popular destination for bird-watchers, as the lake's open expanse of salt pans and sand dunes provide a unique habitat for many species of birds such as pink cockatoos, pelicans, and various species of waterfowl. In the wet season, Lake Amadeus becomes a vast expanse of water. The lake is fed by the Finke River, and water levels can reach up to 8 meters in the center of the lake. The lake is also fed by some smaller rivers, including the Hugh River, the Blackstone River, and the Georgina River.
Lake Argyle is a massive reservoir located in the East Kimberley region of Western Australia. The lake covers an area of over 703 square km. The lake was formed in 1971 when the Ord River Dam was built. The lake is fed by the Ord River and other smaller creeks and rivers. It has a capacity of 10,717 gigalitres, making it the largest reservoir in Australia. The lake has a maximum width of 67 km and maximum width of 10 km. It is surrounded by rugged landscapes and is home to a variety of wildlife, including crocodiles and turtles. Lake Argyle is a popular destination for tourists, with plenty of activities to enjoy.
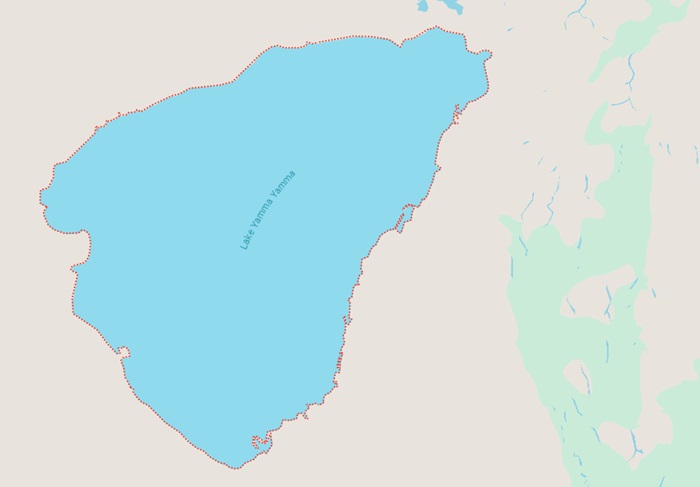
Lake Yamma Yamma is a large lake located in the Northern Territory of Australia. It is the largest inland ephemeral lake in Queensland. The lake has an area of 720 square km. Lake Yamma Yamma is also known as the 'Roper Sea' as it sits within the drainage basin of the McArthur River, which is known as the Roper River. The lake itself is situated in the traditional lands of the Garrwa, Yanyuwa and Marra Aboriginal people. The lake has a long history of being an important site for the local Aboriginal people, who have inhabited the area for thousands of years.
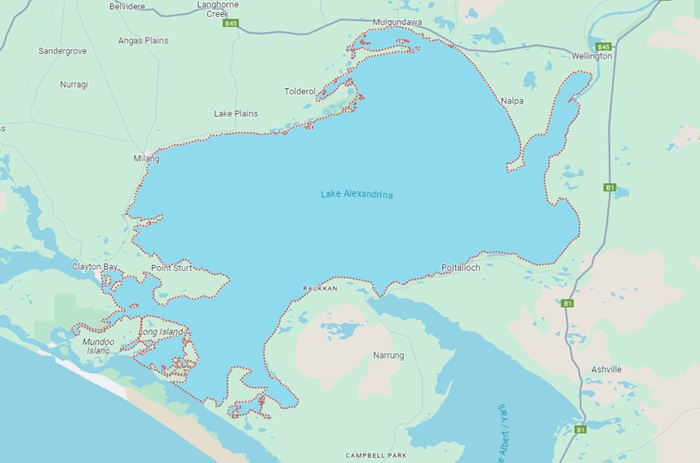
Lake Alexandrina is a large, shallow lake located in South Australia. It is the lower part of the Murray-Darling Basin, which is one of the largest river systems in the world. The lake has an area of 650 square km. Lake Alexandrina is fed by the Murray River and empties into the sea through the Murray Mouth. The lake is home to a wide variety of fish species and other aquatic life. The lake has a maximum depth of around 6 meters, making it relatively shallow compared to other large lakes. The lake is abundant in bird life, with over 200 species being recorded in the area.